This is an excerpt from our most recent Economic Outlook report. To access the full PDF, please click here.
On September 8th, 2025, I asked Google Gemini’s AI tool a pointed macro question:
“Why is the U.S. Household Unemployment Rate Rising in 2025?”
This was the full set of responses to that specific U.S. macro question:
“The U.S. household unemployment rate is rising in 2025 due to a combination of factors, including a slowdown in job growth and increased labor force participation, with the August 2025 rate ticking up to 4.3%.”
Key contributors include:
1. Increased Labor Force Participation
More people are entering the workforce, with the labor force participation rate increasing.
This influx of new job seekers, some of whom may be facing AI-driven job displacement or difficulty re-entering the market after the pandemic, contributes to a higher unemployment rate as it takes time for new workers to find jobs.
2. Economic and Policy Uncertainty
Tariffs imposed by the Trump administration and legal challenges to these policies have created business uncertainty, impacting hiring and leading to a slowdown in overall job growth.
Persistent inflation above the Federal Reserve's target has put pressure on businesses and the economy.
3. AI's Impact on Employment
Advances in Artificial Intelligence are reducing the number of entry-level jobs, particularly for college graduates.
This technological shift, which can affect cognitive tasks, is leading to job displacement in sectors previously considered secure.
4. Sector-Specific Weakness
The manufacturing sector has seen job losses for several consecutive months, a trend linked to tariff uncertainty.
Federal government job cuts are also contributing to the overall weakened labor market conditions.
What unique factor jumped out from this causal list? AI’s impact on employment!
Silicon Valley’s Info Tech industry is deeply embedded in the 2025 California economy.
That led me to dig deeper. Into St. Louis Fed (FRED) Household Unemployment statistics. In search of a multi-dimensional labor market perspective on California, vis-a-vis the rest of the USA.
Chart 1: Vis-à-vis the rest of the USA (the solid blue line), the California Unemployment Rate (the broken green line) always moves up more, cyclically…
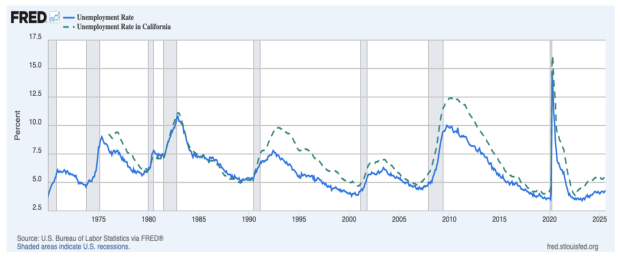
Image Source: St Louis Federal Reserve
Chart 2: In July 2025, the U.S. Unemployment Rate by Metro Statistical Area (MSA) identifies the MSA’s of California as relatively weaker than the Nation, too.
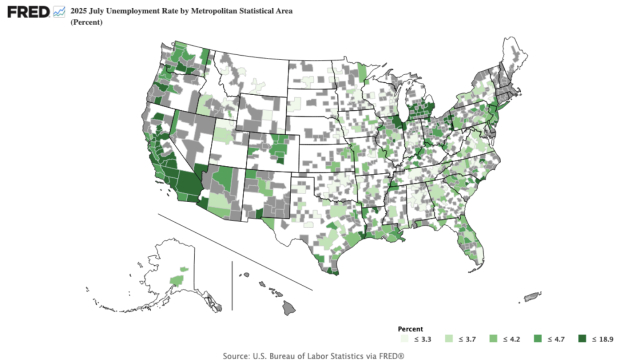
Image Source: St Louis Federal Reserve
At this stage, in my formal inquiry, I wanted to look deeply into this rise in the California household unemployment rate, to 5.5% in August 2025.
Has a respected economist explored, in detail, why there is an August 2025 5.5% California rate, 1.2% in excess of a 4.3% U.S. Household Unemployment Rate?
A recently published article I found online then struck home…
The Economic Outlook for California at Mid-Year
“AI is Already Affecting the Labor Markets”
By Mark Schniepp, July 2025
“The key issue emerging for the California economy in 2025 is the broad-based weakness of the labor market. Only 3 sectors are responsible for all of the job creation this year, and two of the three are either entirely or largely financed by public sector funding—healthcare and local government. Up to now, these two sectors have been mostly unaffected by the recent advent of Artificial Intelligence.”
“As AI tools and technologies continue to advance, companies are increasingly exploring ways to leverage AI to enhance productivity, automate certain tasks, and reduce cost. This includes roles in sales and customer interaction, which may be affected by the increasing efficiency of AI systems.”
“Displacement of jobs by AI is no longer a warning; it has become a reality.”
- “Microsoft announced on June 19, 2025 that thousands of layoffs will occur in July with the sales team taking the largest hit. On July 2nd, the company confirmed that 9,000 workers would be laid off. Last month, Microsoft cut 3 percent of its global workforce, or 6,000 workers. Amid these cuts, the company is investing $80 billion in AI infrastructure and data centers.”
- “IBM announced 8,000 layoffs in late May, mostly in HR, with 9,000 more layoffs planned.”
- “Intel also announced in June that it would lay off 10,000 workers or about 20 percent of its foundry workforce. Those layoffs are occurring this month to streamline operations and eliminate human bureaucracy with more automated systems. Other tech companies like Amazon, Meta and Google have also been implementing workforce reductions and restructuring as they prioritize AI investments.”
“Simply put, AI is automating tasks that are repetitive and time consuming for people. This includes data entry, answering phones, warehouse stock picking and sorting, and assembly line manufacturing, to name a few.”
“By industry, here’s how AI will help business with analytical precision and cost reduction:”
- “Chatbots will handle routine customer inquiries. AI can also categorize and route customer support tickets to appropriate teams or agents. This eliminates administrative support jobs, one of the subsectors of professional business services.”
- “AI can analyze customer behavior patterns in spending data, anticipate where products should be marketed and sold, and make recommendations for business strategies. AI can quickly process large datasets, identifying trend and/or anomalies. The action eliminates intro and mid-level data analysts in the Information labor market of data analytics and processing”
- “AI can evaluate customer interactions with either AI customer service agents or human agents to gauge their emotional state to identify business areas for improvement. Humans doing this now are in the professional business services sector.”
- “AI can power robots and automated systems that handle tasks like packing and sorting goods in warehouse and distribution center settings. Robots will replace warehouse jobs that are part of the transportation and warehouse labor market.”
- “AI currently analyzes data from sensors and equipment logs to predict machine failure rates and develop schedules for maintenance, minimizing downtime and increasing equipment lifespans. Fewer workers are needed in manufacturing to handle these activities to keep assembly lines operating continuously. Jobs in manufacturing are now being eliminated and will continue to be eliminated.”
- “AI can process financial data to automate routine reporting tasks for reports that banks and securities firms need to file with regulating agencies. This will eliminate jobs in the financial activities sector of the broader labor market.”
- “AI can handle facial recognition and object detection for security systems. Business services employment for these tasks can be entirely eliminated.”
- “Chatbots are able to answer customer inquiries and resolve some issues, operating 24/7 without breaks or overtime pay. In fact, no pay.”
“Layoffs that have been the most prolific since the release of ChatGPT have occurred in software programming. AI-powered tools like GitHub Copilot and others can suggest and generate code snippets, functions, or even entire programs. This significantly reduces manual coding efforts and speeds up development. AI-driven tools can analyze code, identify potential bugs and vulnerabilities, and even automatically apply fixes.”
“We have witnessed the loss of 70,000 tech jobs in California since the beginning of 2023; 18,000 of those are in software development. We have also witnessed the elimination of 50,000 jobs in TV, Film and Sound recording, also since early 2023.”
“AI is rapidly advancing in areas like 3D modeling, character design, and environment design, displacing traditional modelers, designers, the need for expensive sets or filming on location. Google Veo 3 is a video generation model that produces cinematic visuals, voice generation and lip-syncing for characters, and adding ambient sound and music. It is designed for businesses to produce short films and ads. AI-powered tools including Veo are accelerating video editing, special effects creation, script writing, animation, art in general, and many post-production tasks, which has led to the need for fewer professionals and technicians in these areas.”
“Surveys have shown that AI has already displaced many workers in the information, entertainment, and gaming industries, and that it has also created new job opportunities. However, at this point, the layoffs appear to have far offset jobs created.”
“Yet the labor market shows very little trauma as a result. Despite minimal job creation in California this year, the unemployment rate is 5.3 percent (5.5% in August) and relatively stable over the last 12 months. It has actually declined modestly since December.”
“As AI matures in tandem with the physical capabilities of autonomous vehicles, taxi drivers, uber drivers, bus drivers, and truck drivers will be largely eliminated. As robotics that lift, move, and sort continue to advance, the factory and warehouse workforce will be meaningfully reduced.”
“The aging population of the state (and nation) is demanding more human healthcare resources than AI can currently displace. Healthcare is the only private labor market that has consistently created jobs over the last 5 years. But even here, AI is now capable of replacing social workers, therapists, nursing assistants, and laboratory technicians. This will undoubtedly begin to reduce the rate of positive job growth that we’ve been observing in California healthcare since 2020.”
“Employment in all other industries is now consolidating, largely due to the rapid onset of AI.”
“While California’s population was in decline between 2019 and 2022, a turnaround occurred with modest growth in 2023 and 2024. This was entirely driven by a rebound in immigration across the southern border. In early 2025, border security was strengthened, resulting in fewer new immigrants arriving at southern and northern entry points.”
“As the decline in California’s population resumes (due to few new immigrants and deportations of illegal immigrants), limited labor force growth will coincide with the AI induced slowdown in job growth. Unemployment is very likely to rise in California in the second half of 2025 and 2026, but significant trauma is not in the forecast.”
AI's Impact Emerges: A 5.5% California Unemployment Rate
This is an excerpt from our most recent Economic Outlook report. To access the full PDF, please click here.
On September 8th, 2025, I asked Google Gemini’s AI tool a pointed macro question:
“Why is the U.S. Household Unemployment Rate Rising in 2025?”
This was the full set of responses to that specific U.S. macro question:
“The U.S. household unemployment rate is rising in 2025 due to a combination of factors, including a slowdown in job growth and increased labor force participation, with the August 2025 rate ticking up to 4.3%.”
Key contributors include:
1. Increased Labor Force Participation
More people are entering the workforce, with the labor force participation rate increasing.
This influx of new job seekers, some of whom may be facing AI-driven job displacement or difficulty re-entering the market after the pandemic, contributes to a higher unemployment rate as it takes time for new workers to find jobs.
2. Economic and Policy Uncertainty
Tariffs imposed by the Trump administration and legal challenges to these policies have created business uncertainty, impacting hiring and leading to a slowdown in overall job growth.
Persistent inflation above the Federal Reserve's target has put pressure on businesses and the economy.
3. AI's Impact on Employment
Advances in Artificial Intelligence are reducing the number of entry-level jobs, particularly for college graduates.
This technological shift, which can affect cognitive tasks, is leading to job displacement in sectors previously considered secure.
4. Sector-Specific Weakness
The manufacturing sector has seen job losses for several consecutive months, a trend linked to tariff uncertainty.
Federal government job cuts are also contributing to the overall weakened labor market conditions.
What unique factor jumped out from this causal list? AI’s impact on employment!
Silicon Valley’s Info Tech industry is deeply embedded in the 2025 California economy.
That led me to dig deeper. Into St. Louis Fed (FRED) Household Unemployment statistics. In search of a multi-dimensional labor market perspective on California, vis-a-vis the rest of the USA.
Chart 1: Vis-à-vis the rest of the USA (the solid blue line), the California Unemployment Rate (the broken green line) always moves up more, cyclically…
Image Source: St Louis Federal Reserve
Chart 2: In July 2025, the U.S. Unemployment Rate by Metro Statistical Area (MSA) identifies the MSA’s of California as relatively weaker than the Nation, too.
Image Source: St Louis Federal Reserve
At this stage, in my formal inquiry, I wanted to look deeply into this rise in the California household unemployment rate, to 5.5% in August 2025.
Has a respected economist explored, in detail, why there is an August 2025 5.5% California rate, 1.2% in excess of a 4.3% U.S. Household Unemployment Rate?
A recently published article I found online then struck home…
The Economic Outlook for California at Mid-Year
“AI is Already Affecting the Labor Markets”
By Mark Schniepp, July 2025
“The key issue emerging for the California economy in 2025 is the broad-based weakness of the labor market. Only 3 sectors are responsible for all of the job creation this year, and two of the three are either entirely or largely financed by public sector funding—healthcare and local government. Up to now, these two sectors have been mostly unaffected by the recent advent of Artificial Intelligence.”
“As AI tools and technologies continue to advance, companies are increasingly exploring ways to leverage AI to enhance productivity, automate certain tasks, and reduce cost. This includes roles in sales and customer interaction, which may be affected by the increasing efficiency of AI systems.”
“Displacement of jobs by AI is no longer a warning; it has become a reality.”
“Simply put, AI is automating tasks that are repetitive and time consuming for people. This includes data entry, answering phones, warehouse stock picking and sorting, and assembly line manufacturing, to name a few.”
“By industry, here’s how AI will help business with analytical precision and cost reduction:”
“Layoffs that have been the most prolific since the release of ChatGPT have occurred in software programming. AI-powered tools like GitHub Copilot and others can suggest and generate code snippets, functions, or even entire programs. This significantly reduces manual coding efforts and speeds up development. AI-driven tools can analyze code, identify potential bugs and vulnerabilities, and even automatically apply fixes.”
“We have witnessed the loss of 70,000 tech jobs in California since the beginning of 2023; 18,000 of those are in software development. We have also witnessed the elimination of 50,000 jobs in TV, Film and Sound recording, also since early 2023.”
“AI is rapidly advancing in areas like 3D modeling, character design, and environment design, displacing traditional modelers, designers, the need for expensive sets or filming on location. Google Veo 3 is a video generation model that produces cinematic visuals, voice generation and lip-syncing for characters, and adding ambient sound and music. It is designed for businesses to produce short films and ads. AI-powered tools including Veo are accelerating video editing, special effects creation, script writing, animation, art in general, and many post-production tasks, which has led to the need for fewer professionals and technicians in these areas.”
“Surveys have shown that AI has already displaced many workers in the information, entertainment, and gaming industries, and that it has also created new job opportunities. However, at this point, the layoffs appear to have far offset jobs created.”
“Yet the labor market shows very little trauma as a result. Despite minimal job creation in California this year, the unemployment rate is 5.3 percent (5.5% in August) and relatively stable over the last 12 months. It has actually declined modestly since December.”
“As AI matures in tandem with the physical capabilities of autonomous vehicles, taxi drivers, uber drivers, bus drivers, and truck drivers will be largely eliminated. As robotics that lift, move, and sort continue to advance, the factory and warehouse workforce will be meaningfully reduced.”
“The aging population of the state (and nation) is demanding more human healthcare resources than AI can currently displace. Healthcare is the only private labor market that has consistently created jobs over the last 5 years. But even here, AI is now capable of replacing social workers, therapists, nursing assistants, and laboratory technicians. This will undoubtedly begin to reduce the rate of positive job growth that we’ve been observing in California healthcare since 2020.”
“Employment in all other industries is now consolidating, largely due to the rapid onset of AI.”
“While California’s population was in decline between 2019 and 2022, a turnaround occurred with modest growth in 2023 and 2024. This was entirely driven by a rebound in immigration across the southern border. In early 2025, border security was strengthened, resulting in fewer new immigrants arriving at southern and northern entry points.”
“As the decline in California’s population resumes (due to few new immigrants and deportations of illegal immigrants), limited labor force growth will coincide with the AI induced slowdown in job growth. Unemployment is very likely to rise in California in the second half of 2025 and 2026, but significant trauma is not in the forecast.”